6-Benzylaminopurine
| Product name | 6-Benzylaminopurine |
| Chinese alias | Adenine,N-benzyl-; Benzyladenine; benzylaminopurine; Cytokinin B; N6-Benzyladenine; N-(phenylmethyl)-1H-purin-6-amine; Purin-6-amine, N-(phenylmethyl)-; Verdan senescence inhibitor; Kinetin( 6-Furfurylaminopurine); 6-BA; AE; 6-Benzylaminopurine(6-BA); 6-benzyladenine; 6-(n-Benzyl) Aminopurin; N-Benzyl-adenine; 2-Benzylaminopurine; N-benzyl-7H-purin-6-amine; N-benzyl-5H-purin-6-amine |
| CAS NO | 1214-39-7 |
| Molecular formula | C12H11N5 |
| Structural formula | 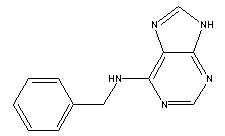 |
| Molecular weight | 225.2492 |
| Physico-chemical properties | White crystalline powder, insoluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, stable in acid and alkali solutions. The physical and chemical properties of 6-BA in pure products are white crystals, while industrial products are white or light yellow, odorless. The pure product has a melting point of 235 ℃, is stable in acids and alkalis, and is not easily decomposed by light and heat. The solubility in water is low, at 60 milligrams per liter, and it is relatively high in ethanol and acid |
| Use | It is a broad-spectrum plant growth regulator that can promote plant cell growth, inhibit the degradation of plant chlorophyll, increase the content of amino acids, and delay leaf aging |